



 NEXT
NEXT
 BACK
BACK
 Forum
Forum


Philosophical musings on Quanta & Qualia; Materialism & Spiritualism; Science & Religion; Pragmatism & Idealism, etc.



Post 120. November 29, 2021
Holism and FreeWill
Versus Reductionism and Fatalism
When a forum poster accused me of being a woo-
Holism and Evolution :
“The holistic approach to life has had such a far-
___review of book by Jan Smuts
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B00VISSWR6/ref=dp-
Another divergence in our philosophy is between Determinism, narrowly defined, and FreeWill, as the ability to choose based on rational evidence rather than on fatalistic necessity. But Determinism is a belief and a premise, not an objective fact. And Determinists typically assume a linear chain of physical causes only. Yet they ignore the influence of feed-
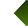
Feedback Loops :
The human brain is a negative feedback loop system. This means that whenever there is a difference between what a person experiences in reality that is different from the ideal set point established by this person’s brain, an urge to behave to correct the situation is created by the brain. https://www.funderstanding.com/brain/brain-
Every Effect has a Cause, but not all causes come from the environment. When faced with an incongruency, humans are able to "leap" to a conclusion that seems reasonable, in light of our prior beliefs of what ought to be true. So, what seems reasonable is not just pure Logic, but can also be determined by any prejudices, premises, and presumptions in our belief system. Those inner beliefs are not in any sense physical objects. Instead, they are meta-
Blog Post 119 continued . . .
continued . . .
1. Meta-
Physics is the science of material Reality. Meta-
2. Beliefs :
Our beliefs are imaginary pictures of Reality that we use to govern our behavior. In the Feedback Loop quote, it is labeled our “ideal set point”. That’s what we think ought to be Real, but is what I call Ideality.
METAPHYSICS
“The central problem of Metaphysics is the existential status of ideas.”
___Bob Doyle,
the Information Philosopher
“Metaphysics is a difficult branch of Philosophy, but is rather easy to define: It is the study of the most fundamental concepts and beliefs about them. Examples of metaphysical concepts are Being, Existence, Purpose, Universals, Property, Relation, Causality, Space, Time, Event, and many others. They are fundamental, because all other concepts and beliefs rest on them. All Knowledge and Value is based upon the definitions of these concepts.”
http://getwiki.net/-
What is Metaphysics? • What is Real? • Metaphysics, inquires, presupposes some theory of what is real, and of what exists? • Metaphysics is closely related to Epistemology; in the same way that Epistemology asks, What is Knowledge and how does it differ from opinion/belief? Metaphysics asks, What is Reality and how it differs from mere appearance? • What is Reality and what are the standards or criteria for what count as REAL? • Both Eastern and Western Traditions have similar definitions of REALITY, that is what is PERMANENT, UNCHANGING, and UNCAUSED can be real.
https://www.slideserve.com/layne/what-


The
Philosophy
Forum
“I don't believe your understanding that all mental phenomena are considered metaphysical is consistent with any generally accepted definition of the word”.
— T Clark
https://thephilosophyforum.com/discussion/12096/what-
Holism vs Reductionism
Synthesis
vs
Analysis

Feedback Loop Learning

Chaotic Progress
positive & negative feedback loops
reinforce & weaken the chain of causation
X
X
Set Point
New Point